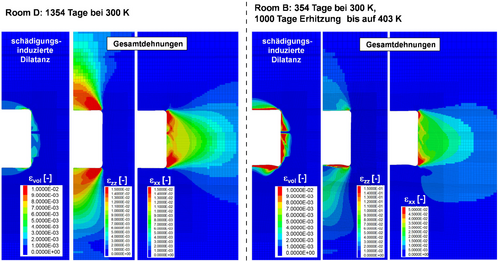
For many geomechanical issues, the propagation of heat or fluids and their effect on stresses and deformations must be considered, e.g., in the case of
- Final disposal of heat-generating waste,
- Injection and withdrawal of gases in storage caverns,
- Assessment of the barrier integrity of final repositories and mines,
- possible extraction of brine from decomissioned caverns.
In these cases, thermo-mechanical (TM), hydro-mechanical (HM), or even fully thermo-hydro-mechanical (THM) coupled calculations may be necessary.
| Dilatance (left) and pressure-driven percolation (right) around a gas storage cavern over several storage cycles. |